Understanding the Mineral Exploration Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction to Mineral Exploration
Mineral exploration is a crucial process in the mining industry, serving as the gateway to discovering new mineral deposits. Understanding this process is vital for stakeholders, investors, and anyone interested in the industry. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the various stages involved in mineral exploration.

Stage 1: Preliminary Research
The exploration process begins with preliminary research. This involves reviewing existing geological data, historical exploration records, and regional maps. Companies assess the potential of areas by analyzing geological surveys and existing mineral occurrences.
Conducting Desktop Studies
Desktop studies are an essential part of preliminary research. These studies focus on gathering and reviewing available data to identify areas with promising mineral potential. The goal is to narrow down large regions to specific targets for further exploration.

Stage 2: Field Exploration
Once promising targets are identified, field exploration begins. This stage involves a more hands-on approach, with geologists and exploration teams conducting on-site investigations. Fieldwork includes mapping, sampling, and geophysical surveys.
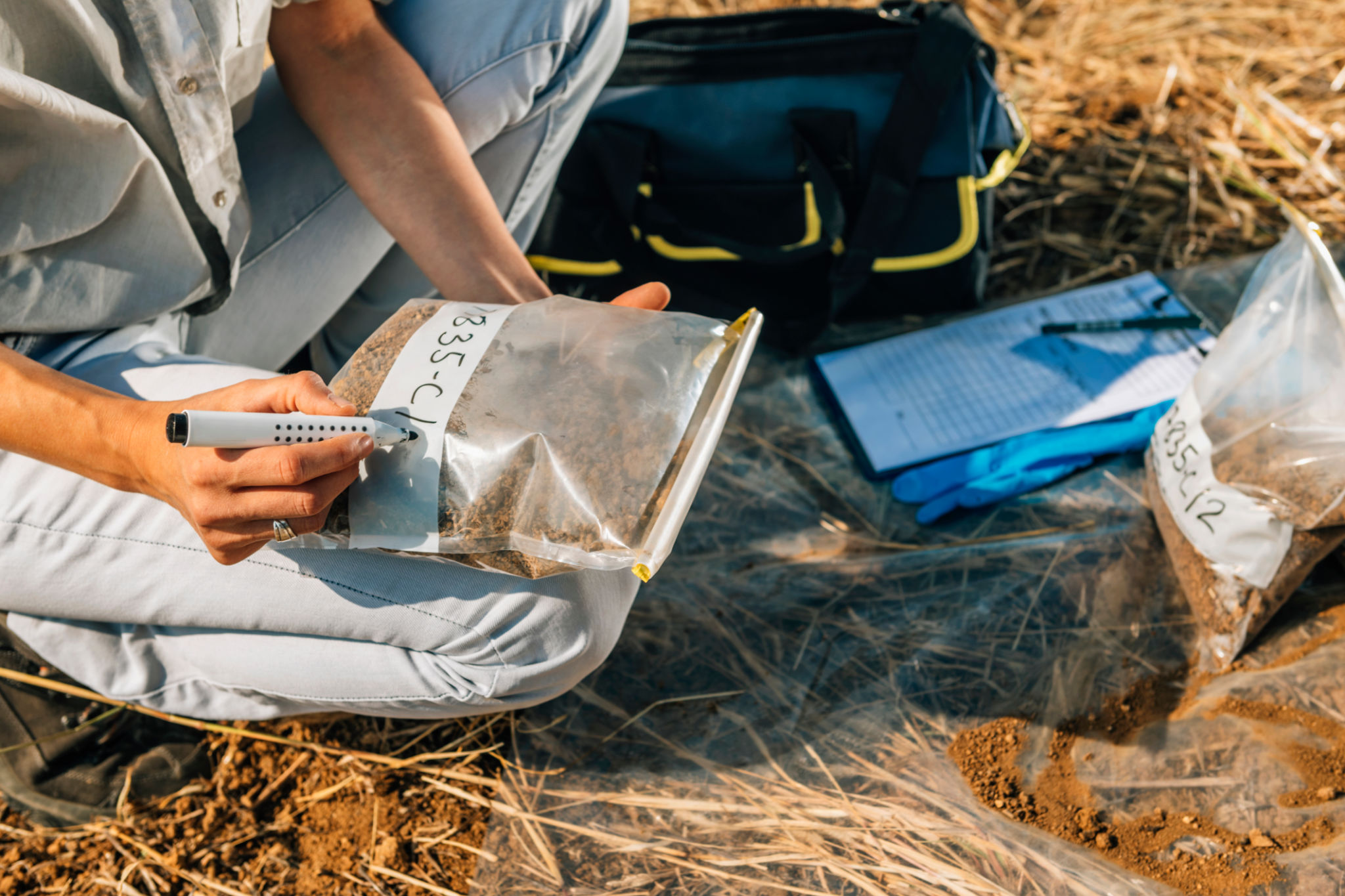
Geochemical Sampling
Geochemical sampling is a crucial component of field exploration. By collecting soil, rock, and water samples, scientists can analyze the chemical properties to detect anomalies that indicate mineral presence. This helps in refining the target areas for drilling.

Stage 3: Drilling and Analysis
After identifying precise target areas, the next step is drilling. Drilling provides a direct look into the subsurface, allowing geologists to confirm the presence and quantity of minerals. This stage is often the most expensive and time-consuming part of the exploration process.
Core Sampling
Core sampling involves extracting cylindrical sections of rock from the earth, which are then analyzed for mineral content. This provides detailed information about the geology and structure of the deposit.
Stage 4: Resource Estimation
Once drilling and analysis are complete, the next step is to estimate the mineral resources. Resource estimation involves calculating the size and quality of the mineral deposit using data from drilling and sampling. This is crucial for determining the project's economic feasibility.

Stage 5: Feasibility Study
A feasibility study assesses whether a mineral deposit can be economically mined. It includes detailed evaluations of the technical, environmental, and financial aspects of a potential mining project. This study helps in making informed decisions about moving forward with mining operations.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Part of the feasibility study involves conducting an environmental impact assessment. This ensures that the potential mining activities comply with environmental regulations and minimize ecological disruption.
Conclusion
The mineral exploration process is complex and involves multiple stages, from initial research to feasibility studies. Each step is crucial to determine the viability of a mineral deposit and its potential for development. Understanding these stages helps stakeholders make informed decisions and contributes to the responsible development of mineral resources.