What Minerals Are Mined in Zambia? An In-Depth Exploration
Zambia is renowned for its rich mineral resources, making it one of the leading producers of minerals in Africa. This landlocked country boasts a diverse range of minerals, each contributing significantly to its economy. In this exploration, we dive into the various minerals mined in Zambia and their impact.
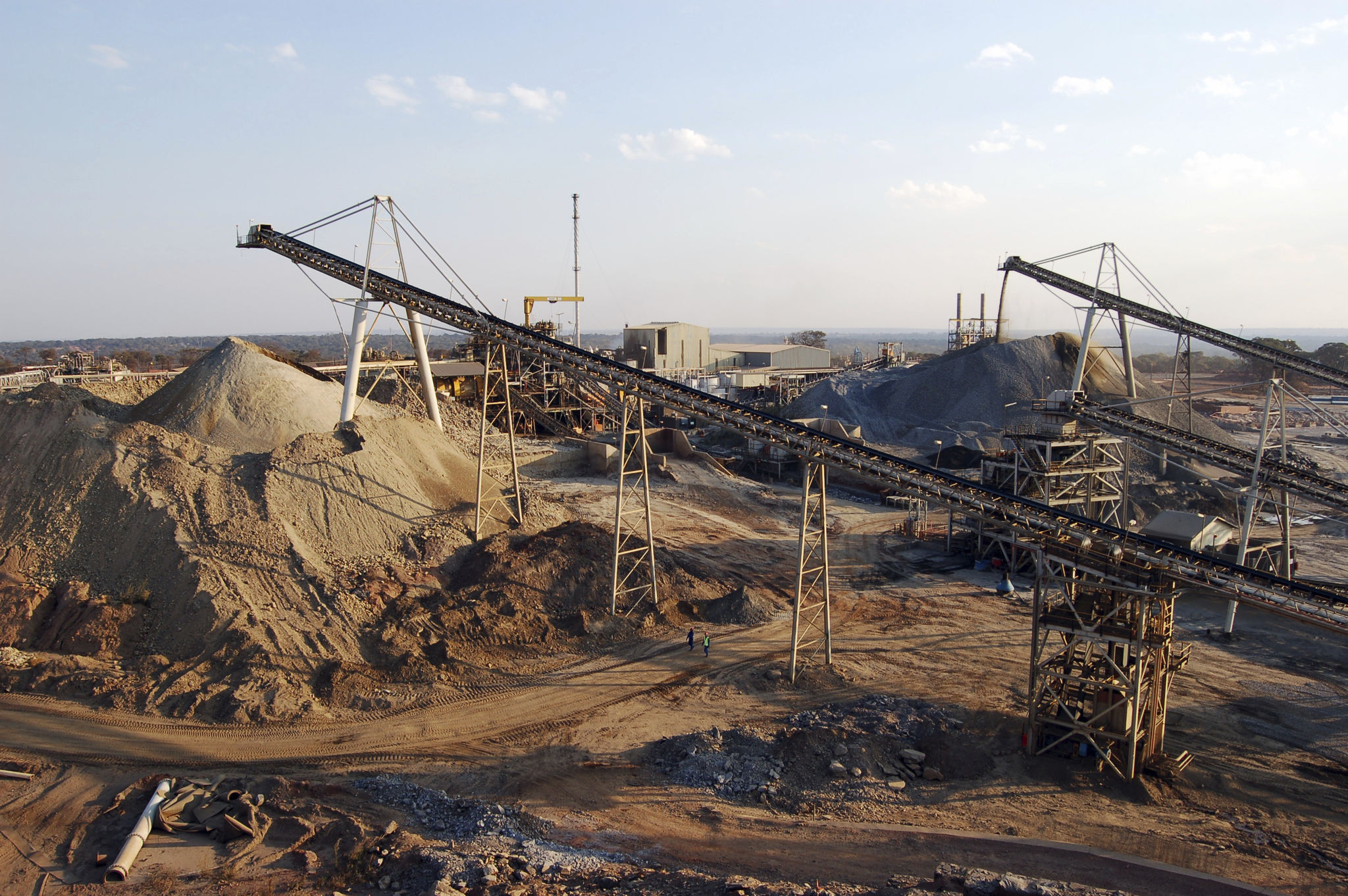

Copper: The Cornerstone of Zambia’s Economy
Copper has been the bedrock of Zambia’s mining industry for decades. The country is one of the world's largest producers of this essential metal. Copper is predominantly mined in the Copperbelt Province, an area that has been at the heart of Zambia's mining sector since the early 20th century.
The significance of copper to Zambia cannot be overstated. It accounts for a substantial portion of the country's GDP and export earnings. This mineral is crucial in various industries, including electronics and construction, making it a valuable asset.
Cobalt: A Byproduct with High Demand
Often extracted as a byproduct of copper mining, cobalt is another critical mineral for Zambia. The increasing global demand for batteries, especially for electric vehicles, has heightened the importance of cobalt. Zambia’s reserves contribute significantly to the global supply, enhancing the country's economic stature.

Emeralds: Precious Gems from Zambia
Zambia is also a major player in the global gemstone market, particularly for emeralds. The Kagem Mine is renowned for producing some of the world's finest emeralds. These gemstones are highly sought after for their vivid green color and clarity, making them a lucrative export for Zambia.
The emerald mining industry provides numerous jobs and stimulates local economies, while also contributing to Zambia's reputation as a premier gemstone producer.
Other Notable Minerals
In addition to copper, cobalt, and emeralds, Zambia is home to other significant minerals:
- Nickel: Found in various regions, nickel mining is growing due to its use in stainless steel and batteries.
- Gold: Although not as dominant as copper, gold mining has seen increased activity, contributing to local economic development.
- Coal: Used mainly for energy production, coal mining supports Zambia's industrial sector.

The Economic and Environmental Impact
The mining sector is a cornerstone of Zambia's economy, providing employment and driving infrastructure development. However, it also poses environmental challenges. Efforts are underway to ensure sustainable mining practices to protect Zambia’s natural landscapes.
Through innovation and regulation, Zambia aims to balance economic growth with environmental stewardship, ensuring that future generations benefit from its rich mineral resources.
Conclusion
Zambia's mineral wealth is a powerful engine for its economic development. From copper to gemstones, these resources offer immense potential for growth. As the global demand for minerals continues to rise, Zambia's mining industry is poised to play a pivotal role in meeting these needs while striving for sustainability.